Powertrain
Overview
The Powertrain manages the complete drivetrain system from engine to wheels using a physically accurate solver based on torque and angular velocity.
Core Components:
- EngineComponent - Power source generating torque from throttle input
- ClutchComponent - Manages engagement between engine and transmission
- TransmissionComponent - Gear ratios for power delivery optimization
- DifferentialComponent - Distributes torque between outputs (wheels or other differentials)
- WheelComponent - Final power sink converting torque to motion

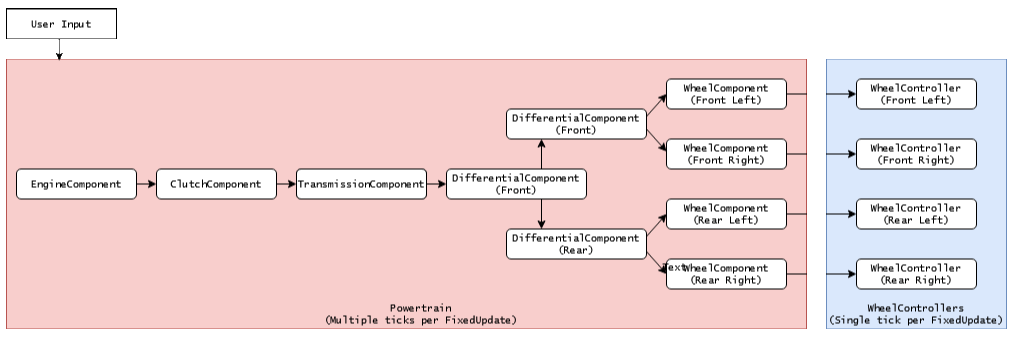
Component Chain
Components connect in a graph-based structure where torque flows from engine through the drivetrain to wheels:
Engine → Clutch → Transmission → Differentials → Wheels
Each component outputs to one or more downstream components, except WheelComponent which outputs to WheelController. The solver uses a two-pass approach:
- Backward pass: Query angular velocities from wheels to engine
- Forward pass: Propagate torque from engine to wheels
Wheel Groups
Wheel groups organize wheels into logical axles for shared steering, braking, and handbrake control:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
steerCoefficient |
How much steering input affects this axle (0-1) |
brakeCoefficient |
Brake force distribution (0-1) |
handbrakeCoefficient |
Handbrake application strength (0-1) |
addAckerman |
Enable Ackermann steering geometry |
Typical Setup:
- Front axle:
steer=1.0, brake=1.0 - Rear axle:
steer=0, brake=0.7, handbrake=1.0
Setup
Automatic Setup
VC_SetDefaults() automatically finds WheelControllers and creates:
- Wheel components in front-to-back, left-to-right order
- Wheel groups based on axle positions
- Default differential configuration (front, rear, center)
- Component connections
Wheel Ordering Requirement: Wheels must be ordered front-to-back (Z descending), then left-to-right (X ascending). Example: Front-Left, Front-Right, Rear-Left, Rear-Right.
Component Connections
Connect components via the Output property in inspector dropdowns. Common configurations:
- 2WD: Single differential → two wheels
- 4WD/AWD: Center differential → front/rear differentials → wheels
Damage System
Each component has a Damage property (0-1):
- 0.0 - Full efficiency
- 0.3-0.7 - Significant performance loss
- 0.7-1.0 - Severe damage, possible failure
Use Repair() to reset all component damage to zero.
Substepping Integration
The powertrain solver runs synchronized with wheel physics through the WheelController substepping system. VehicleController implements ISubstepCallback to execute powertrain calculations before each wheel substep (typically 4x per frame at 50Hz = 200Hz effective).
Benefits:
- Accurate torque delivery responding to wheel state changes
- Smoother clutch engagement and gear changes
- Better stability during rapid RPM changes