Aerodynamics Module
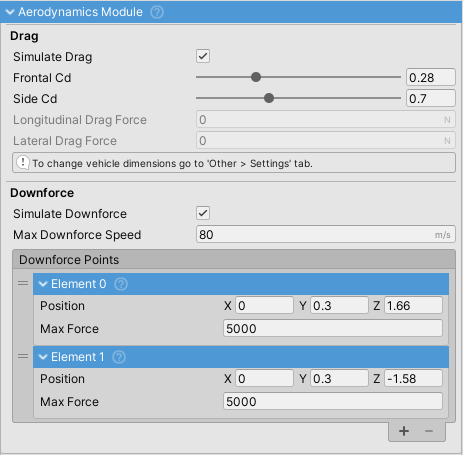
Simulates aerodynamic drag and downforce forces on the vehicle.
Drag
Drag is calculated using the standard aerodynamic equation: F = 0.5 * rho * A * Cd * v^2
- rho: Air density (1.225 kg/m³ at sea level)
- A: Frontal or side area (calculated from vehicle dimensions)
- Cd: Drag coefficient (
Frontal CdorSide Cd) - v: Velocity in the respective direction
Drag forces are calculated separately for:
- Longitudinal (forward/backward motion): Uses
Frontal Cdand frontal area (width * height * 0.85) - Lateral (side-to-side motion): Uses
Side Cdand side area (height * length * 0.8)
Vehicle dimensions are configured under VehicleController > Settings tab (changed in v14).
Drag Coefficients
Typical Frontal Cd values (reference):
- Sports cars: 0.25-0.35
- Sedans: 0.3-0.4
- SUVs/Trucks: 0.35-0.5
- Buses/Large vehicles: 0.6-0.8
Typical Side Cd values: 0.8-1.5 (generally higher than frontal due to less aerodynamic profile).
Damage Integration
When the vehicle has a DamageHandler component, additional drag is applied based on damage:
Damage Drag Effect: Multiplier for extra drag when fully damaged (default: 0.5 = +50%)- Scales linearly with damage level (0 to 1)
- Simulates aerodynamic penalty from damaged bodywork
Performance
Forces are set to 0 when vehicle speed is below 1 m/s to avoid unnecessary calculations.
Downforce
Downforce is applied at configurable points on the vehicle to increase tire grip at high speeds.
- Force increases quadratically from 0 to
Max Downforce Speed, then remains constant - Formula: actualForce = maxForce * (speed / maxDownforceSpeed)^2
- Not dependent on vehicle dimensions, only on configured points and speed
Downforce Points
Each point has:
- Position: Local coordinates relative to vehicle transform
- Max Force: Maximum force in Newtons at max downforce speed
Positioning guidelines:
- Place points low on the vehicle (at wheel height or lower)
- High positions create excessive pitch moments and handling instability
- Typical setup: One point at front axle, one at rear axle
- Front-biased: Reduces understeer at speed
- Rear-biased: Improves stability
Force recommendations by vehicle type:
- Street cars: 100-500 N per point
- Sports cars: 500-2000 N per point
- GT/Touring cars: 2000-5000 N per point
- Formula/Race cars: 5000-10000+ N per point
Ensure suspension spring rates can handle maximum downforce to avoid bottoming out.
Visualization
Enable Gizmos to see downforce points as red spheres in the Scene view.
Properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
Simulate Drag |
Enable/disable drag calculation (default: enabled) |
Simulate Downforce |
Enable/disable downforce calculation (default: disabled) |
Frontal Cd |
Coefficient of drag for frontal area (0-1) |
Side Cd |
Coefficient of drag for side area (0-2) |
Max Downforce Speed |
Speed in m/s where downforce reaches maximum value |
Damage Drag Effect |
Additional drag multiplier when fully damaged (0-5) |
Downforce Points |
List of positions and forces for downforce application |
Longitudinal Drag Force |
Current forward/backward drag in Newtons (read-only) |
Lateral Drag Force |
Current side-to-side drag in Newtons (read-only) |